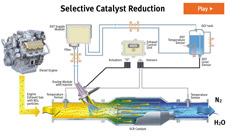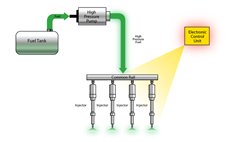
The fuel injection system is a major area of focus for advancement towards clean operating diesel engine. HPCR is an advanced fuel injection design that regulates fuel pressure and injection timing.
Although HPCR was added to many Doosan machines in Tier 3, its ECU is critical for future Interim Tier 4 and Tier 4 technologies.
Fuel Pressure
- The pump applies high pressure to fuel (22,000 - 34,000 psi)
- The common rail stores pressurized fuel
- The injectors deliver fuel to the engine
Injection Timing
The electronic control unit (ECU) precisely controls injectors to allow multiple fuel injections during each combustion cycle.
HPCR Benefits
High pressure transforms fuel into extremely fine mist as it leaves the injectors. Fuel mist combusts (burns) more thoroughly.
- Lower Operating Costs: When fuel combusts more thoroughly, less fuel is needed to run the engine. The result is improved fuel economy.
- Cleaner Exhaust: More thorough combustion leaves less leftover fuel in the exhaust. The result is cleaner exhaust.
When fuel is injected multiple times during each combustion cycle, the combustion lasts longer to create more energy and lower peak engine cylinder pressure.
- Better Performance: Creating more energy during combustion results in more torque output from the engine.
- More Operator Comfort: Lower peak engine cylinder pressure reduces engine noise levels.
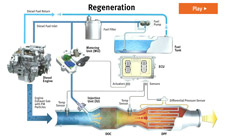
Diesel Oxidation Catalysts (DOC) and Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF)
DOC/DPF systems are highly effective at reducing particulate matter (PM) contained in engine exhaust.
 English
English